 Neuropathy, also known as peripheral neuropathy, is a condition that affects the peripheral nervous system, which consists of the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. It occurs when there is damage or dysfunction to these peripheral nerves, leading to a variety of symptoms.
Neuropathy, also known as peripheral neuropathy, is a condition that affects the peripheral nervous system, which consists of the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. It occurs when there is damage or dysfunction to these peripheral nerves, leading to a variety of symptoms.
The peripheral nerves are responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body, including the muscles, organs, and sensory receptors. They play a crucial role in motor function, sensation, and autonomic functions (such as heart rate and digestion).
Neuropathy can affect a single nerve (mononeuropathy) or multiple nerves (polyneuropathy). It can also be categorized based on the specific types of nerves affected, such as sensory, motor, or autonomic nerves. The most common form of neuropathy is peripheral polyneuropathy, which involves damage to multiple peripheral nerves. Let's explore causes, symptoms, treatments, and the essential nutrients needed for helping defeat neuropathy.
Causes of Neuropathy: Neuropathy can have various causes, including:
-
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves over time, leading to diabetic neuropathy.
-
Trauma: Injuries, accidents, or repetitive stress on nerves can result in nerve damage.
-
Infections: Certain infections, such as Lyme disease, shingles, and HIV/AIDS, can cause neuropathy.
-
Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Guillain-Barré syndrome can lead to nerve damage.
-
Nutritional Deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamins (especially B vitamins), minerals (such as magnesium), and other nutrients can contribute to neuropathy.
-
Toxic Exposures: Exposure to toxins like heavy metals, certain medications, and chemotherapy drugs can damage nerves.
-
Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have inherited genetic mutations that make them more susceptible to neuropathy.
-
Food Intolerance: Consuming foods that contain ingredients that individuals are intolerant to, such as gluten found in wheat, can put them at a higher risk of developing neuropathy.
Symptoms of Neuropathy:
The symptoms of neuropathy can vary depending on the type and location of the affected nerves. Common symptoms include:
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the hands, feet, or other affected areas.
- Sharp or burning pain.
- Muscle weakness or loss of coordination.
- Sensitivity to touch or temperature changes.
- Loss of reflexes.
- Balance problems.
- Digestive issues.
- Changes in blood pressure or heart rate.
Treatment Options:
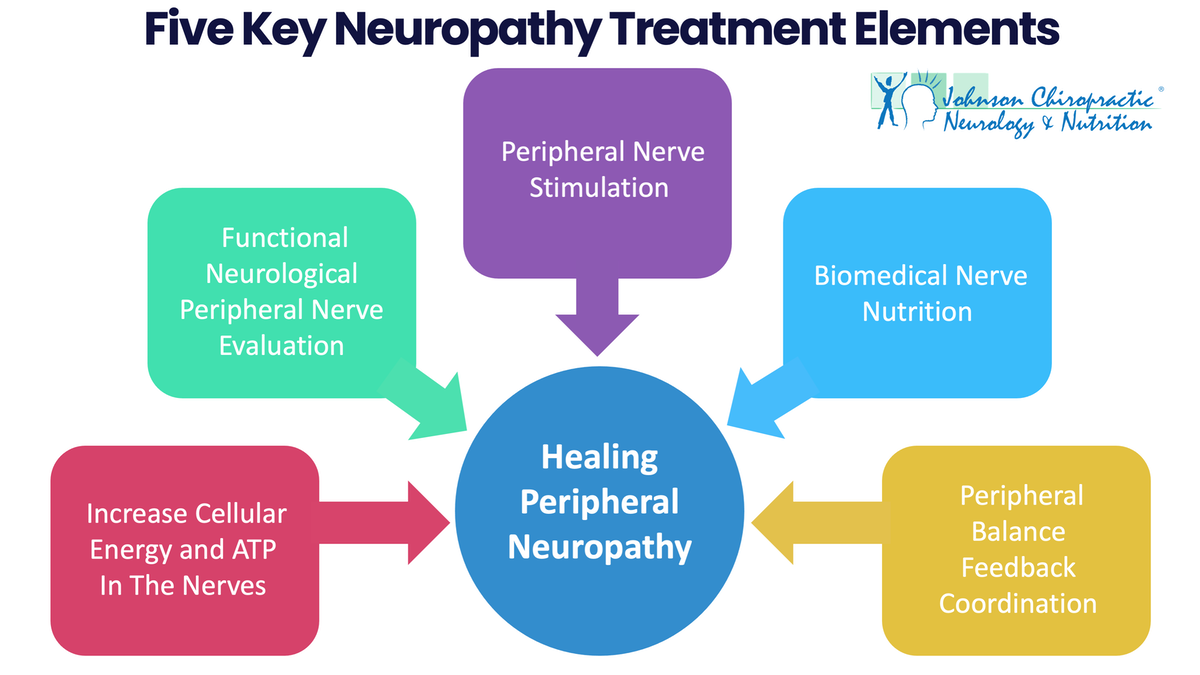
There are several treatment options available for neuropathy, depending on the underlying cause and the specific symptoms experienced by the individual. Here are some common treatments for neuropathy:
-
Medications:
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage mild to moderate pain.
- Prescription medications: Certain medications, such as anticonvulsants (e.g., gabapentin, pregabalin), antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, duloxetine), and opioids (e.g., tramadol), may be prescribed to alleviate neuropathic pain.
- Topical treatments: Medications like lidocaine patches or capsaicin creams can provide localized pain relief.
-
Physical Therapy:
- Exercise programs: Engaging in regular physical activity and specific exercises can help improve muscle strength, balance, and coordination, which can alleviate neuropathy-related symptoms.
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS): TENS therapy involves the use of low-voltage electrical currents delivered through electrodes placed on the skin to provide pain relief and improve nerve function.
-
Nerve Stimulation:
- Spinal cord stimulation: In some cases of chronic neuropathic pain, a spinal cord stimulator device is surgically implanted to deliver electrical signals to the spinal cord, helping to reduce pain signals.
- Peripheral nerve stimulation: Similar to spinal cord stimulation, this involves implanting a device near the affected peripheral nerve to deliver electrical impulses that block pain signals.
-
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Maintaining a healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, especially B vitamins, can support nerve health.
- Elimination inflammatory foods: Removing foods that your immune system is intolerant to or that you have allergies to is essential for managing neuropathy. It's worth noting that gluten intolerance, in particular, has been identified as a potential cause of idiopathic neuropathy.
- Managing underlying conditions: Effective management of conditions like diabetes, autoimmune diseases, or infections can help prevent or slow down the progression of neuropathy.
- Pain management techniques: Techniques such as relaxation exercises, meditation, and biofeedback may help individuals cope with neuropathic pain.
-
Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture: The insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body may provide pain relief and improve nerve function in some individuals.
- Herbal remedies: Certain herbal supplements, such as alpha-lipoic acid or evening primrose oil, have shown potential in reducing neuropathic pain, but further research is needed.
- Dr. Karl R.O.S. Johnson, DC's Breakthrough Neuropathy Program.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs and the underlying cause of neuropathy.
Nutritional Supplements for Reducing Neuropathy
While medical and/ or a combination of alternative treatment is crucial, certain nutritional supplements can complement conventional therapies and support nerve health. Let's explore several evidence-based supplements that may assist in reducing neuropathy symptoms and promoting overall nerve well-being. Please note that it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating any supplements into your regimen.
-
Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA):
- ALA is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect nerve cells from oxidative stress.
- Studies have shown that ALA supplementation can alleviate neuropathic symptoms and improve nerve conduction velocity.
- Dosage: 600-1,200 mg per day. Split the dosage into two or three smaller doses for better absorption.
- References:
- Ziegler D, et al. (2011). Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a meta-analysis. Diabetic Medicine, 28(4), 450-461.
- Papanas N, et al. (2018). Efficacy of α-lipoic acid in diabetic neuropathy. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy, 19(6), 597-605.
- References:
-
Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALC):
- ALC helps enhance nerve regeneration and supports mitochondrial function.
- Research suggests that ALC supplementation may alleviate pain and improve nerve function in individuals with neuropathy.
- Dosage: 1,000-2,000 mg per day, divided into two or three doses.
- References:
- Sima AAF, et al. (2013). Acetyl-L-carnitine improves pain, nerve regeneration, and vibratory perception in patients with chronic diabetic neuropathy: An analysis of two randomized placebo-controlled trials. Diabetes Care, 36(5), 414-420.
- Veronese N, et al. (2017). Effect of acetyl-L-carnitine in the treatment of painful peripheral neuropathies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PAIN, 158(7), 1234-1246.
- References:
-
B Vitamins:
- B vitamins, especially B1 (thiamine), B6 (pyridoxine), and B12 (cobalamin), are crucial for nerve health and function.
- Deficiencies in these vitamins have been linked to neuropathy and supplementing with them may help alleviate symptoms.
- Dosage:
- Thiamine: 300 mg per day.
- Pyridoxine: 100-200 mg per day.
- Cobalamin: 1,000-2,000 mcg per day.
- References:
- Rhee EP, et al. (2019). Metabolite profiling identifies markers of uremic neuropathy. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 30(10), 2022-2035.
- Sun Y, et al. (2018). Effectiveness of vitamin B12 on diabetic neuropathy: Systematic review of clinical controlled trials. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 138(6), 459-467.
- References:
-
Magnesium:
- Magnesium plays a crucial role in nerve function and helps regulate nerve signaling.
- Supplementation with magnesium may help reduce neuropathic pain and improve nerve conduction.
- Dosage: 400-800 mg per day, divided into two doses.
- References:
- Guerrero-Romero F, et al. (2015). Oral magnesium supplementation improves glycaemic status in subjects with prediabetes and hypomagnesaemia: A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy, 8, 767-773.
- Zhang X, et al. (2018). Magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes: Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Care, 41(4), 832-839.
- References:
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
- Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce nerve inflammation.
- Studies suggest that supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids can alleviate neuropathic pain and improve nerve function.
- Dosage: 1-4 grams of combined EPA and DHA per day.
- References:
- Maroon JC, et al. (2017). Omega-3 fatty acids (fish oil) as an anti-inflammatory: An alternative to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for discogenic pain. Surgical Neurology International, 8, 236.
- Dworkin RH, et al. (2018). Interventional management of neuropathic pain: NeuPSIG recommendations. PAIN, 159(3), 595-604.
- References:
Conclusion:
While nutritional supplements can play a complementary role in reducing neuropathy symptoms, it is crucial to approach them as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. These supplements, including alpha-lipoic acid, acetyl-L-carnitine, B vitamins, magnesium, and omega-3 fatty acids, have shown promise in supporting nerve health and reducing neuropathic symptoms. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure safety and appropriate dosage for individual needs. By combining these supplements with appropriate medical care and/or alternative care therapies, individuals with neuropathy can take proactive steps toward improving their quality of life and overall nerve well-being.
If you want to find out more, check out what makes my philosophy unique among health care providers.
Always remember one of my mantras, "The more you know about how your body works, the better you can take care of yourself."
For more details about the natural approach I take with my patients, take a look at the book I wrote entitled: Reclaim Your Life; Your Guide To Revealing Your Body's Life-Changing Secrets For Renewed Health. It is available in my office or at Amazon and many other book outlets. If you found value in this article, please use the social sharing icons at the top of this post and please share with those you know who are still suffering with chronic health challenges, despite receiving medical management. Help me reach more people so they may regain their zest for living! Thank you!